What Meaning Does the Triangle Symbol Hold in Medical Notations?
The triangle symbol in the medical field signifies several key concepts. Originally used in anatomical diagrams, it simplifies complex structures, such as the femoral triangle.
It symbolizes balance and stability, echoing the equilibrium necessary for peak health. Historically, it denotes transformation and hierarchical representation in medical documentation, aiding in understanding lineage and genetic inheritance.
The triangle also serves as a critical icon in healthcare communications and patient education, marking hazards and illustrating medical processes like diagnosis and treatment. The multifaceted use of the triangle underscores its importance in medicine—discover more about its profound impact on healthcare practices.

Key Takeaways
- The triangle symbol in medical diagrams often marks anatomical landmarks, like the femoral triangle, for precise identification of structures.
- An equilateral triangle symbolizes balance and stability, which is essential for achieving peak health and homeostasis.
- In healthcare communication, the triangle represents the triad of patient care: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
- Triangles in clinical signage denote hazards and warnings, ensuring clear and swift comprehension of safety information.
- The triangle is used to symbolize hierarchical structures in medical documentation, aiding in the visual representation of relationships and genetic inheritance.
Anatomical Diagrams
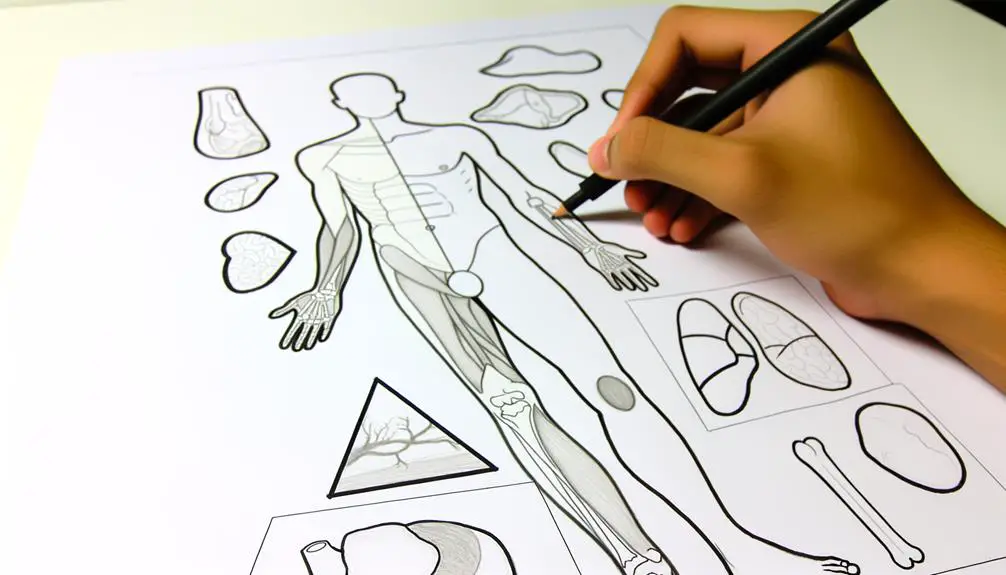
In anatomical diagrams, the triangle symbol is often employed to denote specific anatomical landmarks or regions, providing a visual shorthand that facilitates precise communication among medical professionals.
Historically, this practice dates back to early anatomical studies where simplification was essential for education and reference. For example, the femoral triangle is a well-documented anatomical region demarcated using this symbol, aiding in the identification of critical structures like the femoral artery, vein, and nerve.
The triangular representation allows for quick, unambiguous identification, enhancing both learning and clinical practice. Such usage underscores the symbol's value in reducing complexity, thereby enabling practitioners to focus on intricate details while maintaining clarity and consistency in anatomical illustrations.
Balance and Stability
The equilateral triangle, with its equal sides and angles, epitomizes balance and stability, a concept pivotal in medical diagnostics and anatomical symbolism.
Historically, this geometric form has been employed to represent equilibrium within the human body, reflecting a holistic approach to health.
Analyzing its symbolic representation reveals its pervasive influence on medical imagery and therapeutic practices, underscoring the intersection of geometry and medicine.
Equilateral Triangle Significance
An equilateral triangle, with its equal sides and angles, symbolizes balance and stability in medical contexts, reflecting the holistic equilibrium necessary for peak health.
Historically, the equilateral triangle has been emblematic of harmony and proportion, which are fundamental in achieving physiological homeostasis.
Each side of the triangle can represent a critical aspect of health—physical, mental, and social well-being—echoing the World Health Organization's definition of health.
This geometric shape serves as a visual metaphor for the interconnectedness of these facets, underscoring the necessity of maintaining balance among them for best health outcomes.
In medical practices, this symbolism aids in promoting a thorough approach to patient care, encouraging healthcare professionals to address all dimensions of health.
Symbolic Representation Analysis
Symbolic representation of the equilateral triangle in medical contexts underscores balance and stability, critical concepts that have been deeply rooted in both ancient and modern healthcare paradigms. Historically, the equilateral triangle has been a symbol of equilibrium, reflecting the triadic balance of mind, body, and spirit. This is particularly significant in medical practice, where maintaining stability across these dimensions is essential for holistic well-being. The symmetry of the equilateral triangle further symbolizes structural integrity and robustness, ensuring that the system remains resilient against disruptions.
| Aspect | Symbolic Meaning |
|---|---|
| Equilateral Sides | Equal importance |
| Angles | Consistent measures |
| Center Point | Holistic focus |
| Base | Foundational strength |
| Height | Aspirational goals |
This symbolic analysis highlights the critical importance of maintaining equilibrium within the medical field.
Change and Transformation

Historically, the triangle has symbolized metamorphosis in healthcare, reflecting the dynamic nature of medical advancements and patient recovery. This geometric shape encapsulates the symbolic healing process, where patients shift from illness to health through structured and often transformative interventions.
Analyzing the triangle's representation in medical contexts reveals its profound implications for understanding change and transformation in therapeutic practices.
Metamorphosis in Healthcare
The triangle symbol in medical contexts often signifies change and metamorphosis, reflecting the dynamic nature of healthcare evolution.
Historically, healthcare has undergone significant shifts, from rudimentary practices to advanced, evidence-based medicine. The triangle, with its stable three-point structure, symbolizes the integration of new methodologies, technologies, and paradigms.
For instance, the change from traditional to digital health, encompassing telemedicine, electronic health records, and AI diagnostics, epitomizes this ongoing transformation. The triangle's geometric precision mirrors the systematic approach required for effective healthcare reforms.
These changes are not merely superficial but represent profound shifts in patient care, professional training, and healthcare delivery systems. Understanding the triangle offers a lens into the continuous adaptation and progress within the medical field.
Symbolic Healing Process
Embracing the inherent symbolism of the triangle, the healing process in medicine illustrates a profound journey of change and transformation, intricately linking patient recovery with systemic adaptations in medical practice. Historically, the triangle has represented a trinity of elements, often interpreted in medical contexts as the interaction between the mind, body, and spirit. This triadic relationship underscores the dynamic process of healing, emphasizing holistic integration.
| Element | Significance in Healing |
|---|---|
| Mind | Cognitive and emotional resilience |
| Body | Physical recovery and rehabilitation |
| Spirit | Psychological and spiritual balance |
Through detailed analysis, it becomes evident that addressing these interconnected dimensions fosters comprehensive well-being, promoting not just symptom alleviation, but true transformation in patient health.
Hierarchical Structures
In medical documentation, the triangle symbol often denotes hierarchical structures, indicating relationships such as parent-child connections in family histories or the organization of anatomical information.
Historically, the use of the triangle in genealogical charts has facilitated the visual representation of lineage and genetic inheritance patterns, aiding clinicians in diagnosing hereditary conditions. This geometric symbol also helps in structuring complex anatomical data, where hierarchical categorization is essential for clarity.
For example, the triangle can signify the stratification of tissue layers or the nested relationships among anatomical systems. Employing the triangle in these contexts ensures a streamlined, intuitive understanding of multifaceted medical information, allowing healthcare professionals to quickly discern relational hierarchies essential for patient care and medical research.
Symbolism in Healthcare

Frequently, symbolism in healthcare serves as an essential tool for communication, facilitating the conveyance of complex medical concepts through universally recognized icons. Historically, symbols such as the caduceus and the red cross have played pivotal roles in signifying medical services and humanitarian aid.
The triangle symbol, often associated with warning and caution, historically emerged within public health to denote alertness and urgency. Analyzing its use, the triangle's three sides can represent the triad of patient care: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. This symbolic framework allows healthcare professionals to navigate and articulate intricate medical scenarios effectively.
Consequently, such symbols enhance comprehension among diverse stakeholders, ensuring clarity and precision in critical healthcare communications.
Practical Applications
The practical applications of the triangle symbol in medical contexts are multifaceted, ranging from its use in clinical signage to its role in patient education materials, thereby enhancing both safety and understanding in healthcare environments.
Historically, the triangle has symbolized stability and direction. In modern clinical settings, it frequently appears on cautionary labels, denoting hazards such as biohazardous materials or radiation zones.
Additionally, in patient education, the triangle is employed to represent hierarchical structures, such as the food pyramid or pain management scales. This consistent use in diverse medical facets ensures clarity and promotes swift comprehension.
The symbol's inherent simplicity and geometric precision make it an invaluable tool for conveying critical information effectively in high-stakes healthcare settings.
Conclusion
To conclude, the triangle symbol in medical contexts serves multifaceted purposes, from representing anatomical structures and physiological balance to indicating change, transformation, and hierarchical organization.
Its utilization in healthcare, steeped in historical context and precise terminology, underscores its significance.
The triangle's enduring presence, akin to a linchpin in a complex machine, highlights its essential role in conveying critical information and facilitating practical applications within the medical field.






