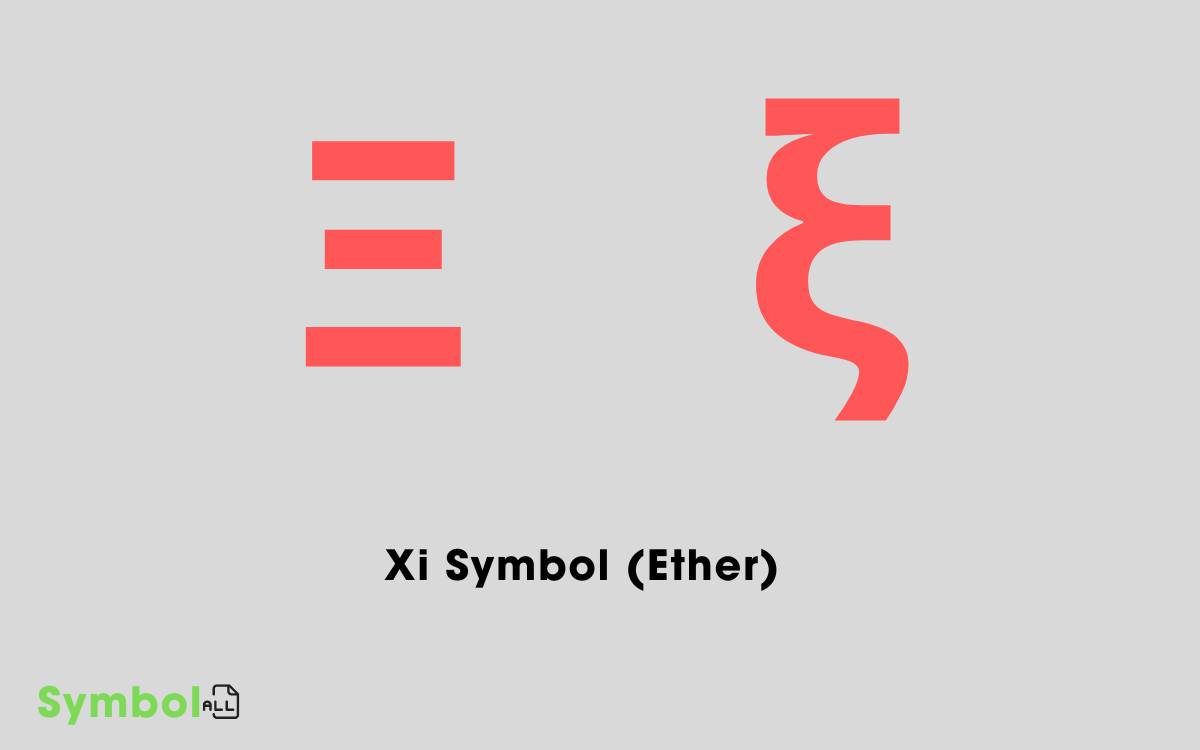
Xi Symbol (Ether)
In your exploration of the xi symbol (ξ), you’ll find it serves crucial roles both in theoretical contexts and in the Ethereum ecosystem.
Originating from the Greek alphabet as the 14th letter, ξ is extensively used in mathematical and scientific disciplines to denote unknown variables and parameters.
It’s distinguished by its unique visual form, which aids in minimizing confusion with more commonly used symbols.
Intriguingly, its significance extends to Ethereum, where ξ symbolizes Ether, the primary cryptocurrency that facilitates smart contracts and decentralized applications on the blockchain.
Understanding its dual usage could unlock deeper insights into both mathematics and digital currency systems.
Xi Symbol (Ether) & Meaning
| Symbol | HTML | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Ξ | ΞΞU+39E | Xi Symbol (Uppercase): The uppercase Xi often appears in contexts such as the twelfth letter of the Greek alphabet. |
| ξ | ξξU+3BE | Xi Symbol (Lowercase): The lowercase xi symbol is employed in diverse scientific areas including physics and mathematics, commonly to represent unknown variables or specific coefficients. |
| ψ | ψψU+3C8 | Psi Symbol: Often seen alongside Xi in mathematical and scientific contexts. |
| ρ | ρρU+3C1 | Rho Symbol: Commonly used to represent density in physics. |
| σ | σσU+3C3 | Sigma: Represents standard deviation in statistics. |
| π | ππU+3C0 | Pi: Denotes the mathematical constant Pi. |
| θ | θθU+3B8 | Theta: Frequently used to indicate angles in trigonometry. |
| ω | ωωU+3C9 | Omega: Used in physics to signify angular frequency. |
| Ω | ΩΩU+3A9 | Omega: Represents the final letter of the Greek alphabet and is also used in electrical engineering to denote ohms. |
Key Takeaways
- The query “Xi Symbol (Ether)” likely refers to the symbol “Ξ”, used to represent the cryptocurrency Ether (ETH) on Ethereum.
- “Ξ” is the uppercase form of the 14th letter of the Greek alphabet, xi.
- In the context of Ethereum, “Ξ” symbolizes Ether, the platform’s native cryptocurrency.
- This symbol is chosen for its distinctiveness and lack of common use in other major contexts.
- The use of “Ξ” aids in distinguishing Ether transactions and balances within Ethereum’s decentralized platform.
Historical Origins of Xi
The symbol Xi, originating from the Greek alphabet, has been adopted in various scientific and mathematical contexts due to its unique properties and versatility. You’ll find Xi particularly prominent in fields like physics and statistics.
In particle physics, Xi denotes a set of subatomic particles known as Xi baryons. These particles are essential for understanding the strong force that holds the nucleus of an atom together.
In statistics, Xi often represents a random variable, providing a foundational element in probability theory and stochastic processes. Its adoption across diverse disciplines underscores its utility in representing complex concepts succinctly.
Understanding its applications can enrich your grasp of these scientific fields, where Xi plays a critical role in theoretical frameworks and empirical research.
Xi in the Greek Alphabet
You’ll find the Xi letter positioned as the 14th character in the Greek alphabet, distinguished by its unique symbol Ξ in uppercase and ξ in lowercase.
Examining its usage, Xi frequently appears in scientific contexts, particularly in mathematics and engineering, to represent variables and parameters.
These examples not only highlight its functional role but also underscore its integration into various academic and professional disciplines.
Xi Letter Overview
Xi, the 14th letter of the Greek alphabet, plays a critical role in various scientific and mathematical contexts. It’s crucial you understand its structure and implications.
Resembling the English letter ‘E’ in lower case (ξ), Xi is distinguished by its unique visual form which contributes to its application in specialized areas.
Here’s a concise table to visually summarize some key aspects:
| Attribute | Description | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Alphabet | Greek | Ξ, ξ |
| Position | 14th letter | – |
| Pronunciation | /ksi/ or /zaɪ/ | – |
| Case Forms | Uppercase (Ξ), Lowercase (ξ) | – |
This structured approach helps you visualize Xi’s role within the Greek alphabet, enhancing your grasp of its uses in broader contexts.
Xi Usage Examples
Often, scholars and mathematicians use Xi to denote unknown variables or parameters in equations and models.
You’ll find it particularly prevalent in fields requiring complex notation, such as quantum mechanics or statistical analysis.
Xi’s distinct shape helps avoid confusion with more commonly used symbols like x or y, providing clarity in textual expressions.
Moreover, in theoretical physics, Xi might represent damping coefficients in oscillatory systems, integrating seamlessly into differential equations that model physical phenomena.
Understanding its usage can significantly enhance your comprehension of mathematical texts where standard variables are insufficient.
Thus, familiarizing yourself with Xi not only broadens your mathematical vocabulary but also deepens your analytical skills in interpreting sophisticated scientific literature.
Ethereum Explained
You must first understand that Ethereum operates as a decentralized platform that supports smart contracts: applications that run exactly as programmed without any possibility of downtime, censorship, fraud, or third-party interference.
These contracts are scripts stored on the blockchain, enabling transparent and secure transactions without intermediaries.
As we explore Ethereum’s network fundamentals, you’ll appreciate how this architecture supports a wide array of distributed applications and new business models.
Ethereum Network Fundamentals
To fully grasp the Ethereum network, it’s crucial to understand that it operates as a decentralized platform enabling smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) to be built and run without downtime, fraud, control, or interference from a third party.
Ethereum is fundamentally designed to use blockchain technology, not only for tracking transactions but also for running programming code of any decentralized application.
Here’s a quick breakdown to clarify the core components:
| Component | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Blockchain | Immutable ledger recording all transactions |
| Ether (ETH) | Primary cryptocurrency used for transaction fees |
| Gas | Unit that measures the computational effort |
| Consensus Model | Ensures security and agreement on the network |
| Node | Individual computer connected to the Ethereum network |
Understanding these elements will deepen your appreciation of how Ethereum functions technically.
Smart Contracts Functionality
Building on the Ethereum network fundamentals, smart contracts automate transactions and agreements, executing automatically when predefined conditions are met.
You’ll find these contracts aren’t merely scripts but are self-operating programs that live on the Ethereum blockchain. They can’t be altered post-deployment, ensuring reliability and trustworthiness.
When you engage with these contracts, you’re interacting directly with the code. Each contract carries its unique address on the blockchain, accessible universally.
Smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing transaction costs and enhancing efficiency.
They’re pivotal in decentralized applications (dApps), where they manage logic and state transitions.
Understanding these mechanisms allows you to leverage Ethereum’s full potential, streamlining operations and enforcing agreements without external enforcement entities.
Ether as Cryptocurrency
Ether serves as the primary cryptocurrency of the Ethereum blockchain, facilitating transactions and decentralized application operations. It’s integral in executing smart contracts, as these self-executing contracts require Ether for the computation resources they consume.
You’ll find that Ether isn’t just a digital currency, but a fuel for the operational capabilities of the Ethereum network.
Transaction fees, known as ‘gas’, are paid in Ether. These fees vary depending on the computational effort, bandwidth, and storage needs of a transaction or contract.
This pricing mechanism mitigates spam transactions and allocates resources efficiently across the network.
Understanding Ether’s role in this ecosystem is crucial for leveraging its full potential within decentralized applications, beyond mere currency functionalities.
The Role of Xi in Ethereum
Understanding the role of Xi in Ethereum is essential as it influences how transactions and smart contracts are processed on the network.
You’ll find that Xi isn’t just a symbol; it represents a critical aspect of Ethereum’s underlying framework.
Here’s how Xi impacts Ethereum:
- Transaction Execution: Xi determines the precision in transaction processing, ensuring accuracy and reliability.
- Smart Contract Deployment: It plays a vital role in the deployment mechanism of smart contracts, affecting their execution efficiency.
- Network Scalability: Xi influences how Ethereum scales, particularly through its role in sharding and state channels.
- Consensus Mechanism: It’s integral to maintaining the consensus mechanism, aiding in the overall security and stability of the Ethereum network.
Grasping these points provides you with a deeper insight into Ethereum’s operational dynamics.
Economic Impact of Ether
Now let’s examine how Ether’s economic impact shapes market dynamics and influences global cryptocurrency practices.
As the native token of the Ethereum platform, Ether acts as a key driver in the world of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. Its integration across various sectors not only facilitates transactional efficiencies but also broadens the scope for financial innovation.
You’ll find that Ether’s liquidity and volatility are pivotal in shaping investment decisions and market strategies. Its demand correlates strongly with the expansion of the Ethereum network, influencing the valuation of other digital assets and cryptocurrencies.
Moreover, Ether’s role in initial coin offerings (ICOs) has been instrumental, providing startups with a mechanism to raise capital, thus fueling further innovation and market expansion.
Technological Significance of Xi
Xi’s technological significance fundamentally reshapes how industries engage with blockchain technology, enhancing both the scalability and efficiency of network transactions.
Here’s why you should care:
- Increased Transaction Speed: Xi’s architecture allows for faster transaction processing compared to traditional blockchain systems.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: It incorporates advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Lower Operational Costs: By optimizing network algorithms, Xi reduces the energy consumption and the associated costs of running blockchain networks.
- Improved Scalability: It supports a larger number of transactions simultaneously without compromising the speed or security of the network.
Understanding these points ensures you grasp how Xi stands at the forefront of evolving blockchain technology, making it pivotal for future developments.
Future Trends in Cryptocurrency
Building on the technological advancements of Xi, future trends in cryptocurrency are set to further revolutionize financial transactions and digital security.
You’ll witness the integration of AI algorithms that enhance blockchain efficiency, predicting market trends with unprecedented accuracy.
Scalability solutions, such as sharding, will allow networks to handle exponentially more transactions, reducing bottlenecks and lowering costs.
You’ll also see increased adoption of zero-knowledge proofs, offering you privacy without sacrificing transparency.
Moreover, regulatory frameworks will mature, fostering wider acceptance while ensuring your protection against fraud.
As these technologies converge, you’re looking at a landscape where digital currencies aren’t just safer; they’re indispensable to global commerce. You must stay informed and adaptive to navigate this rapidly evolving sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Pronounce “Xi” in Different Languages?
In English, you pronounce ‘xi’ as “zee,” while in Mandarin, it’s pronounced like “she.” Greek articulates it as “ksee.” Each language’s phonetic system influences how they interpret and pronounce ‘xi.’
What Are Alternative Symbols or Names for Ether?
Alternative symbols or names for ether include quintessence and aether, historically used in alchemical and philosophical contexts to denote the pure, celestial element believed to fill the universe above the terrestrial sphere.
Can Xi Symbol Be Used in Mathematical Equations?
You can use the Xi symbol in mathematical equations, ensuring it doesn’t conflict with other variable definitions. It’s crucial to define it clearly to maintain precision and avoid ambiguity in your mathematical expressions.
Who First Proposed Using Xi for Ether?
You’re asking who first proposed using a particular symbol for a concept. It was James Clerk Maxwell who introduced the symbol “xi” to denote a specific parameter in his electromagnetic field equations.
Are There Visual Representations or Logos Featuring Xi?
Yes, you’ll find that several logos and visual symbols feature the xi character, blending ancient script with modern design elements to represent various concepts, particularly in fields like mathematics and physics.
Is the Omicron Symbol Related to the Xi Symbol (Ether) in Any Way?
The omicron symbol is not related to the Xi symbol (ether) in any way. Understanding the omicron symbol is important in recognizing the current variant of concern, but it does not have a connection to the Xi symbol used to denote the cryptocurrency ether.
Conclusion
As you delve into the evolving landscape of digital finance, remember that the symbol Xi isn’t just a character; it’s a cornerstone in the robust framework of Ethereum.
Ether, as a pivotal asset, enhances your financial toolkit, offering both challenges and vast potential. Navigating this terrain requires a keen understanding of its intricate mechanics.
Embrace the future of cryptocurrency with an informed perspective, and you’ll find yourself at the forefront of technological innovation and economic evolution.
